Study examines efficacy and possible mechanisms of Botulinum Toxin type A on hypertrophic scarring
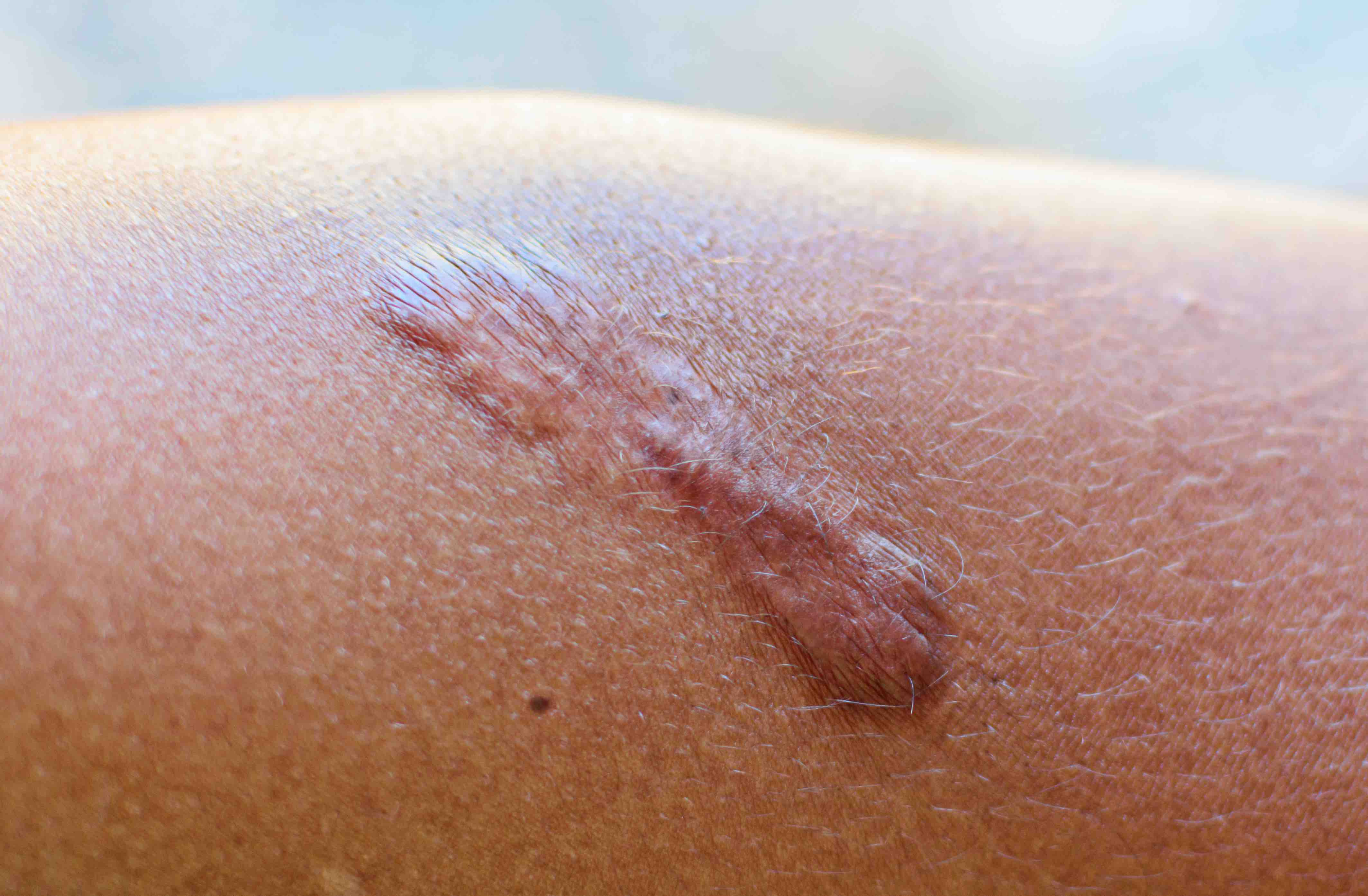 A study published in the April issue of the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology has examined the efficacy and possible mechanisms of botulinum toxin type A (BTX-A) on hypertrophic scarring.
A study published in the April issue of the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology has examined the efficacy and possible mechanisms of botulinum toxin type A (BTX-A) on hypertrophic scarring.
Clinical observations indicate that BTX-A can inhibit the growth and improve the eventual appearance of hypertrophic scarring. The team used human keloid fibroblasts to investigate the molecular mechanism of BTX-A on hypertrophic scarring.
Different concentrations of BTX-A (0.01, 0.1, 1, and 10 U/L) were used to treat keloid fibroblasts.Keloid fibroblast viability decreased with increasing BTX-A dose. After BTX-A treatment, the volume of keloid fibroblast cells increased, but the nucleus of cells shrunk. Long, thin dendrites were formed as the concentration of BTX-A increased.
The authors concluded that BTX-A may promote the healing of scars by inhibiting the proliferation of keloid fibroblasts and regulating the expression of TGF-1, which could affect the expression of MMP-1 and MMP-2. This study provides theoretical support for the clinical application of BTX-A to control hypertrophic scarring.
for more information visit the journal's website here

